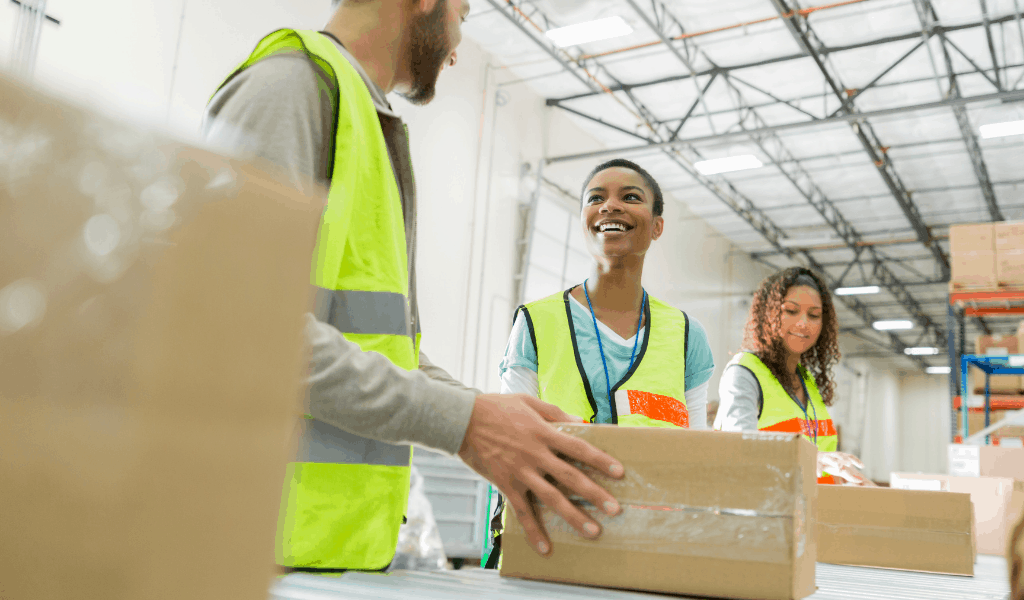
Warehousing services help manufacturers easily handle capacity
What types of manufacturers need warehouses?
Warehouses are a critical component to the supply chain of manufacturers, and each manufacturer requires some amount of warehousing. Warehouses provide manufacturers with the space to store raw materials, WIP goods, and finished goods. Warehouses also perform value added services and other necessary jobs. The warehousing needs of each manufacturer are unique, and different warehouses serve different purposes along the supply chain. Manufacturers of made to stock, made to order, and made to assemble goods all need warehouses at points along their supply chain.

Made to stock (MTS)
Manufacturers of made to stock goods require significant warehousing for their raw materials, WIP goods, and finished goods. Since MTS manufacturers intend to stock their goods prior to sales, the bulk of warehousing is for the finished goods. Finished goods may require storage warehousing, distribution warehousing, cross docking, or other warehousing services.

Made to order (MTO)
Since made to order goods are manufactured once an order is placed, MTO operations are sensitive to lead times and other supply chain delays. MTO manufacturers require various warehousing services from the time the order is placed until the finished goods are delivered to the customer. MTO manufacturers use storage warehouses, fulfillment centers, distribution centers, and other warehouses along their supply chains.
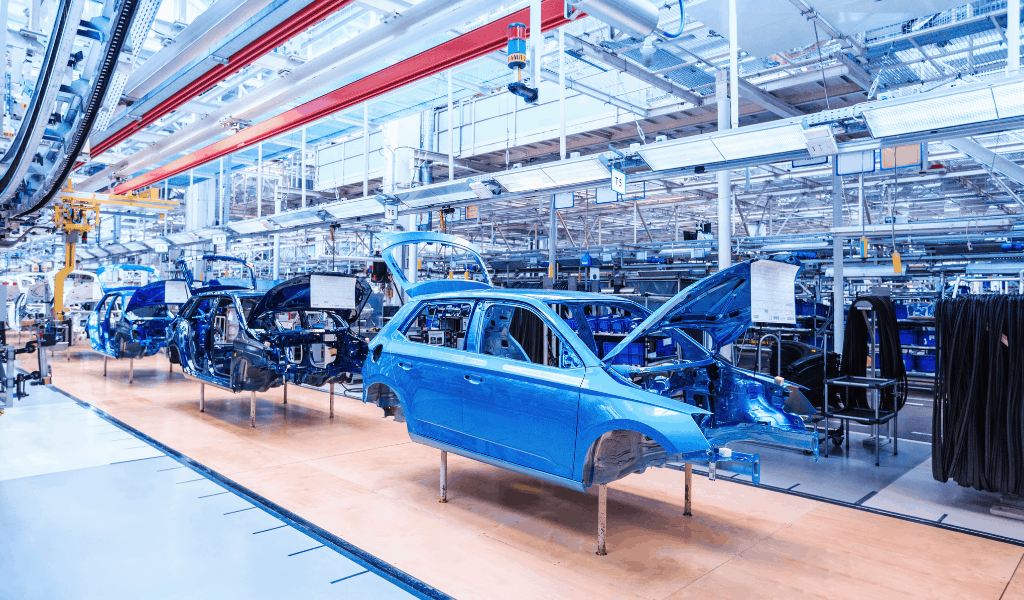
Made to assemble (MTA)
Manufacturers of made to assemble goods use significant warehousing services across their supply chain; WIP goods are the primary driver of MTA manufacturers’ warehouse demand. Additionally, these manufacturers need storage warehousing, distribution warehouses, fulfillment centers, light assembly centers, and other similar services along their supply chain.
What services do warehouses offer?
Warehouses perform a range of services for their clients that is often only limited by their clients’ needs. That is, most warehouses are willing and able to complete any warehouse services that you require for your operation. While these customized warehouse services are available, there are also standard warehousing services offered to clients across the industry.
Transloading & cross docking

Inbound processing

Outbound processing & order fulfillment
Light assembly & kitting

Inventory control

Overflow capacity

Temporary storage

Labelling & repackaging

What are warehousing services?
Warehousing services encompass a wide variety of service offerings performed by warehouse providers. Warehouses offer diverse services to their customers as a win-win for both the client and the warehouse provider, since the client needs different types of work completed and the warehouse is able to perform the different types of needed work.
Services performed by the warehouse are broadly grouped into 5 categories.
- Inbound processing services are the work completed to receive and process all inbound freight.
- Outbound processing services are the work required to pick, pack, and ship all outbound orders.
- Inventory control and management is all work completed to track, manage, and report on inventory levels.
- Value added services are any work performed by the warehouse that alters the state or packaging of goods.
- Storage is the work to safely store and maintain goods within the facility.
What are the benefits of warehousing?

Inventory control
Warehouses diligently manage the inventory in their facility, so clients see exactly how many of each good are in each warehouse. Strict operational processes ensure inventory control is maintained, and that clients have full visibility and reporting of their goods.

Store more of what you need
Warehouses give you a place to store, or stockpile, goods that are in high demand. Strategically selected warehouses ensure that the supply chain runs smoothly, with plenty of safety stock on hand for a minimal cost.

Scalable operations
Warehouses specialize in handling clients’ receiving, storing, and shipping needs so the client can focus on growing their core business. Scalable operations are possible with warehouses that work as your partner to handle your growing needs with ease.
What is the difference between manufacturing and warehouse?
Warehouses and manufacturers work together to achieve a smooth flowing supply chain for end consumers. Manufacturing facilities are where goods are altered, assembled, or produced. Warehouses support manufacturing facilities by storing raw materials, WIP goods, and finished goods that the manufacturing facility does not need or have space for. The supply chain of manufacturing operations need warehouses to provide storage space and handle excess capacity.
Manufacturers turn raw materials and unfinished goods into different, more valuable finished goods through various production and assembly processes. Manufacturing requires some insight or expertise of goods production, and often requires industrial equipment to produce the finished goods. The primary role of warehouses is to store goods and handle them as they are received or ordered out. Warehouses specialize in managing inventory, storing goods, fulfilling orders, and performing value added services. Warehouses are often able to handle many types of goods for many clients in a single facility, so client costs are reduced and diverse warehousing knowledge is readily available.
What is non-manufacturing warehouse?
A non-manufacturing warehouse is a facility that does not alter or produce goods from raw materials and unfinished goods. Instead these warehouses serve as vital processing points for inbound receiving, outbound handling, storage, quality control, inventory control, and more. Raw materials, WIP goods, and finished goods all pass through multiple warehouses during their manufacturing journey to end user.
A non-manufacturing warehouse may offer diverse services or serve only specific functions such as distribution, fulfillment, or storage. Distribution warehouses are used to receive bulk shipments that are then broke into smaller shipments and delivered to multiple destinations. Fulfillment centers pick and pack stored goods as orders are placed; fulfillment centers may service both B2B and B2C clients. Storage warehouses are used to store goods until they are needed for a future date, that may not be specified. Storage warehouses are not regularly staffed because there is little to no inventory transactions at these locations. Many non-manufacturing warehouses will do all of these services, rather than only some of the warehousing services.
How can manufacturers get started
- Contact our team
- Quick call (with a WE owner-operator) to confirm details and client need
- WE send you Rates, and provide a few sample invoice scenarios based on the details gathered during the call
- You award Warehousing Etc the job
- Prepare your shipment(s) for delivery to our Tampa warehouse
- You produce, we warehouse










